Abstract
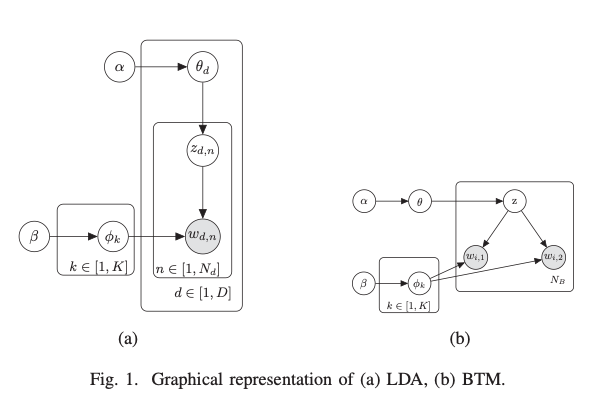
With the popularity of social networks, such as mi-croblogs and Twitter, topic inference for short text is increasingly significant and essential for many content analysis tasks. Biterm topic model (BTM) is superior to conventional topic models in uncovering latent semantic relevance for short text. However, Gibbs sampling employed by BTM is very time consuming when inferring topics, especially for large-scale datasets. It requires O{K) operations per sample for K topics, where K denotes the number of topics in the corpus. In this paper, we propose an acceleration algorithm of BTM, FastBTM, using an efficient sampling method for BTM which only requires O(1) amortized time while the traditional ones scale linearly with the number of topics. FastBTM is based on Metropolis-Hastings and alias method, both of which have been widely adopted in latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model and achieved outstanding speedup. We carry out a number of experiments on Tweets2011 Collection dataset and Enron dataset, indicating that our method is robust enough for both short texts and normal documents. Our work can be approximately 9 times faster than traditional Gibbs sampling method per iteration, when setting K = 1000. The source code of FastBTM can be obtained from https://github.com/paperstudy/FastBTM.